An IR (infrared) sensor is an electronic component that detects and measures the infrared radiation ( IR signals are not observable by the human eye) in its environment. When a human, object, or anything comes closer to the sensor, the IR from the LED reflects off of the object and is detected by the receiver.
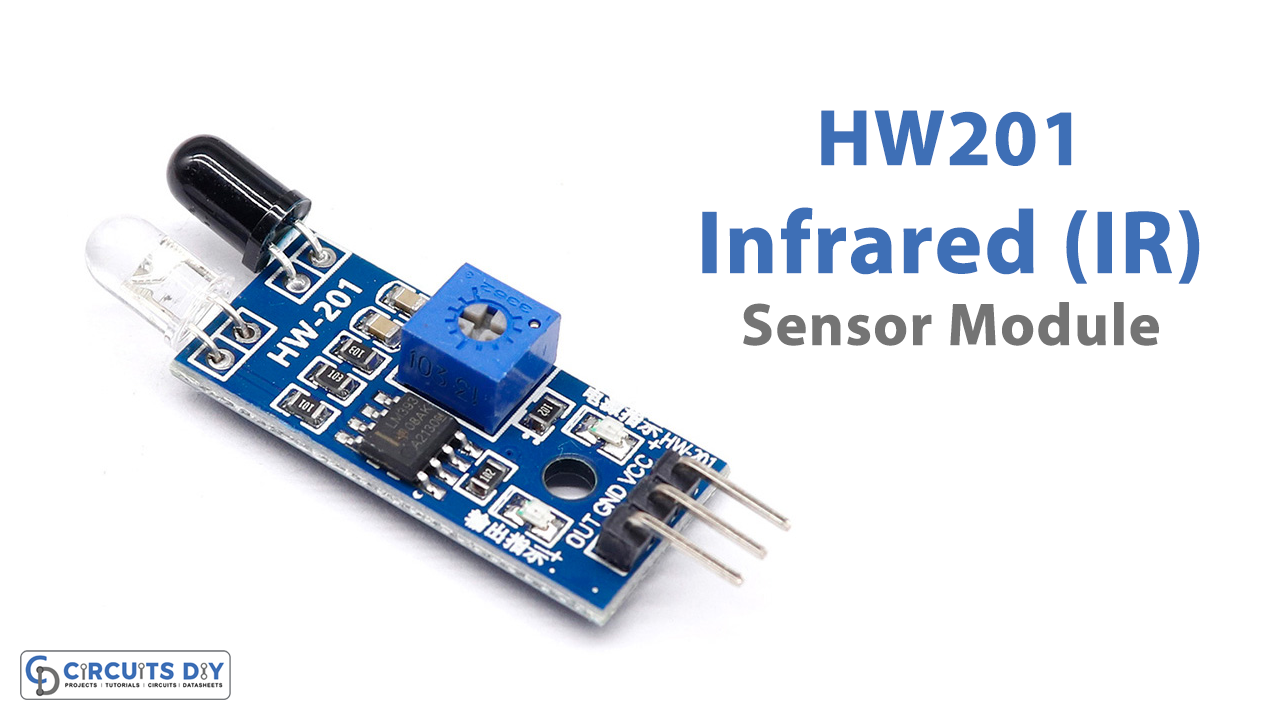
Overview of HW201 Sensor
The HW201 comprises emitting and receiving tubes, transmitting tubes emitting certain infrared frequencies when it detects the obstacle, the sensor has the reception tube which receives that infrared frequency, Then there is a process of the comparator circuit. There is a green light that gets ON after that, The module also has a potentiometer through which one can adjust the detection distance.
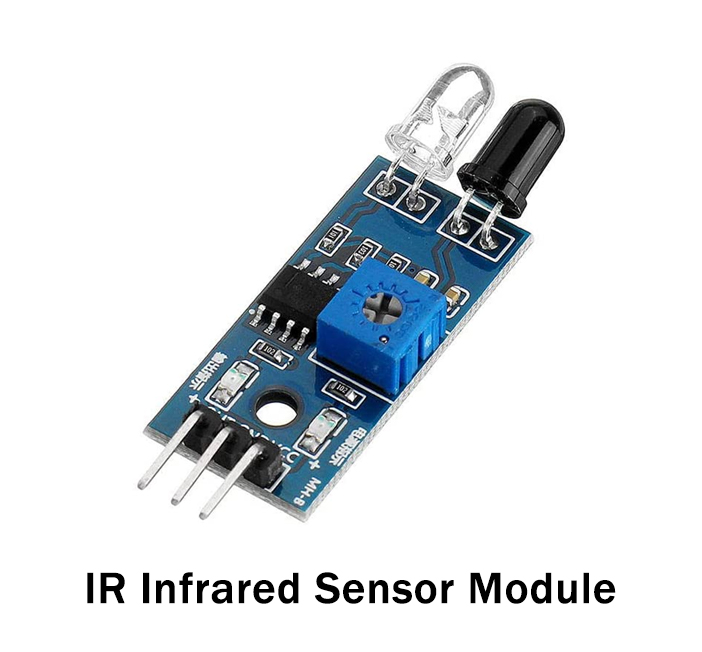

Working
TR Transmitter in the module emits Radiation. And, if the radiation gets reflected, the IR Receiver detects radiation and its resistance drops down, output goes low. If the radiation doesn’t get reflected, the Receiver doesn’t detect any Radiation, therefore its resistance rises, and output goes high.
Features and Specifications
Features
- 2 to 30cm adjustable sensing range (on-board Potentiometer)
- 35-degree Detection Angle
- LM393 Comparator Selection Output
- Easy to use
- Please note that the sensor sensitivity varies depending on the reflection surface applied
Specifications
- Main Chip: LM393
- Detection Distance: 2~30cm
- Detection Angle: 35 °
- Working Voltage: 3.3V~5V
- Board Size: 31 * 14mm / 1.22 * 0.55in
- Board Weight(1pc): 3g
- 20mA supply current

Pinouts of HW201 Module
| Pin Name | Description |
| VCC | Power Supply Input |
| GND | Power Supply Ground |
| OUT | Active High Output |
Applications of IR Sensor
IR Imaging Devices
IR image devices are one of the primary applications of IR modules, primarily because of their property that is not visible. We used it for thermal imagers, etc.
Security Devices
Since the IR module works for infrared radiation, therefore, it may be utilized in some Security devices. The transmitter transmits, and the receiver receives the waves. When something comes between these waves, the receiver gives the signal forward to the circuit.
Other Applications
- Flame monitors
- Obstacle detection devices
- Robotics
- Gas detectors
- Gas analyzers, etc