Introduction
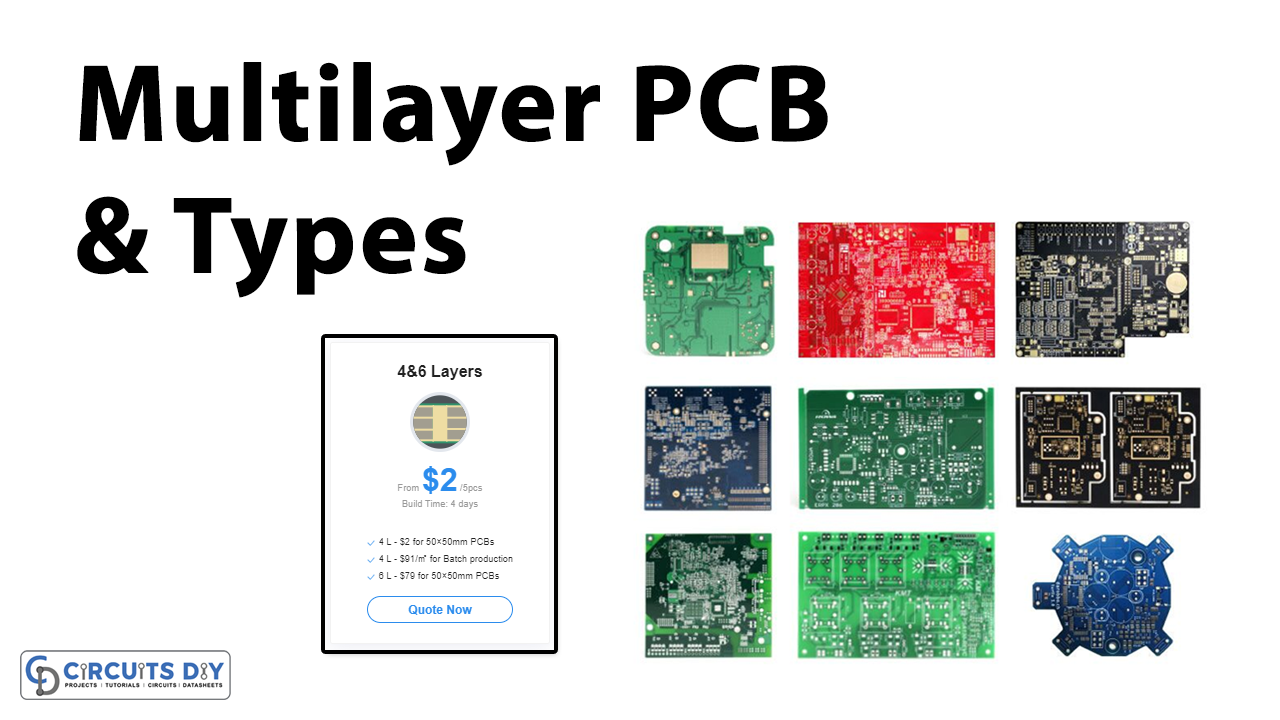
Printed circuit boards are an essential part of any electronic circuitry. And, since most electronic devices have advanced circuitry, therefore the designers go for multilayer PCB instead of one layer. Thus, Multilayer printed circuit boards are gaining popularity. The capacity to create multilayer boards opens up a new world of possibilities for engineers, allowing them to create more densely populated circuit boards, and allowing for downsizing. This is a big benefit that single-layer boards do not have. But, multilayer PCBs are more costly than single-layer PCBs. However, the JLCPCB has made it extremely inexpensive for everybody.

JLCPCB can produce PCBs of different complexity. They make both affordable single-layer PCBs for novices and hobbyists and sophisticated multilayer PCBs for high-quality industrial applications.
JLCPCB manufactures the cheapest yet best quality PCBs. They’re always exploring methods to enhance and speed up the PCB prototype process, from inventing online quoting systems and automated production to quick turnaround.
Layer Stacking
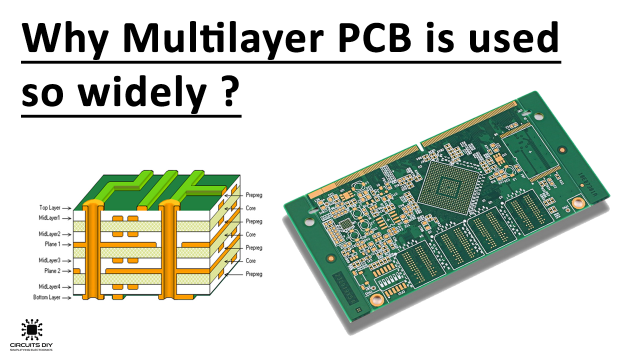
Multi-layer PCBs have three dual-size copper layers, providing for a full ground plane layer. It can support thousands of components and tens of thousands of vias. The majority of multi-layers have less than ten conducting layers and a thickness of 1.5mm. The multilayer includes
- Top layer for electronic components
- Inner layers for routing
- Bottom layer for components

Multilayer PCB Manufacturing Process
- The procedure begins with the creation of the PCB layout using any PCB design software / CAD tool (Proteus, Eagle, OrCAD).
- Ne is to build the Inner Layer. To create the inner layer core, a laminate of the necessary thickness is treated with copper foil, dry filresistancest, and UV light.
- Now the stage is lamination. Inner layer core, prepreg sheets, and copper foil sheets are all part of this process.
- The staking of layers for a four-layer board is as follows: a bottom layer of copper foil – prepreg sheets – inner layer core – more prepreg sheets – the top layer of a copper foil sheet
- The pressure, heat, and vacuum are then applied using a heated hydraulic press. It is critical to vacuum to ensure that no air is trapped between the layers. This procedure concludes around 2 hours depending on n number of layers.
- When the resins from the prepregs cure, they join the sheets, core, and foil together to make a multilayer PCB.
Advantages of Multilayer PCB
- Light Weight: The construction of multi-layePCBsCB is less in weight as compared to the other types of PCBs.
- Small Size: These PCBs certainly have a small size because of the design. As we all know that recent and modern electronic needs smaller sizes. So, the compact sizes of PCBs help in making smaller devices.
- High Durability Rate: multi-layer PCBs easily withstand high pressure and thermal expansion. So, it increases the durability of circuits.
- One Connection Point: Rather than multiple connection points, it only has one connection point
- High Speed: The close-quarter enables the board to be more connective. As all the components are near to each other. Consequently, results in a higher speed.
Disadvantages of Multilayer PCB
- Cost: These boards are more expensive than regular boards. It is used primarily in aerospace and high-tech products for a reason. This is perhaps the major drawback of ceramic circuit boards.
- Handling: They are difficult to handle and need extra effort. As a result, if it is damaged, it will take a long time to repair.
- Limited Manufactures: There are limited manufacturers available and some cost higher. However, er as we discussed earlier the JLCPCB has made it extremely inexpensive for everybody.
Uses of Multilayer PCB
- Computers and Laptops
- Telecommunications Equipment – Mobile Phone, Tablets, and other Hand Help Devices
- File server and Data storage
- Signal transmission, mobile phone repeaters, GPS
- Satellite
- Medical Equipment: Testing, X-Ray, Heart Monitor, CAT Scan
- Industrial Equipment
- Atomic and Nuclear Systems
- Military and Defense Equipment
- Automotive
- Aerospace
- Anywhere, where complex Circuitry is needed.