We all know the importance of power supplies in electronics. In our previous articles, we have already learned about their huge number of applications and uses in electronic devices and circuits. Yet, most of the power supplies we studied and built used transformers in their circuits. But, in this tutorial, we will make a “Transformerless Power Supply 6V DC.”
You’ll likely come across transformerless supplies at some point in your life since they are used in various products, from LED lights to WiFi switches. So, below we’ll examine their inner workings and discuss their design and construction.
What is Transformerless Power Supply?
A TPS, which stands for “transformerless power supply,” is just a voltage divider. This device takes 115 or 220 VAC and lowers it to whatever voltage the user specifies. If that voltage must be DC, it is rectified using a few diodes.
Hardware Required
| S.no | Component | Value | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Diode | 1N4007 | 4 |
| 2. | Polyester Capacitor | 474K/400V | 1 |
| 3. | Zener Diode | 6.2v | 1 |
| 4. | MOV (Metal Oxide Varactor) | – | 1 |
| 5. | LED | – | 1 |
| 6. | Fuse | – | 1 |
| 7. | Capacitor | 1000uF | 1 |
| 8. | Resistor | 1K, 470K, 100R, 120R | 1, 1, 1, 1 |
| 9. | Power Supply | – | 1 |
| 10. | Fuse | 6A | 1 |
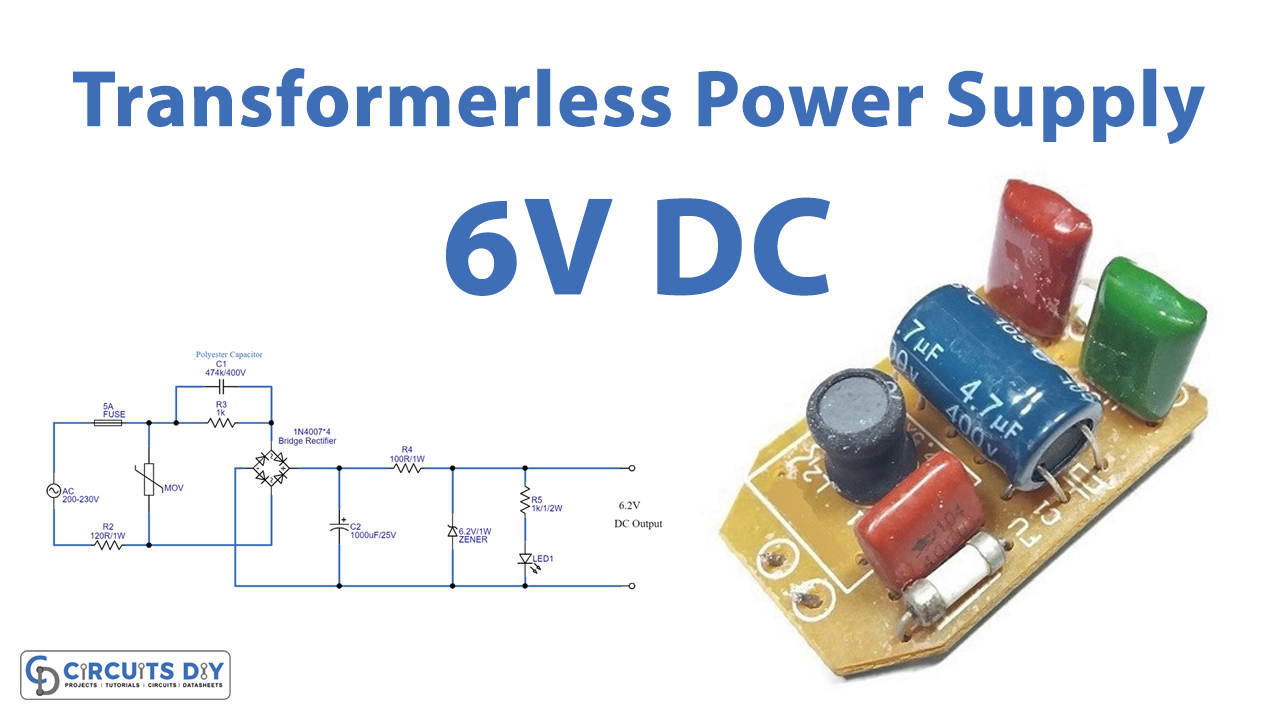
Circuit Diagram
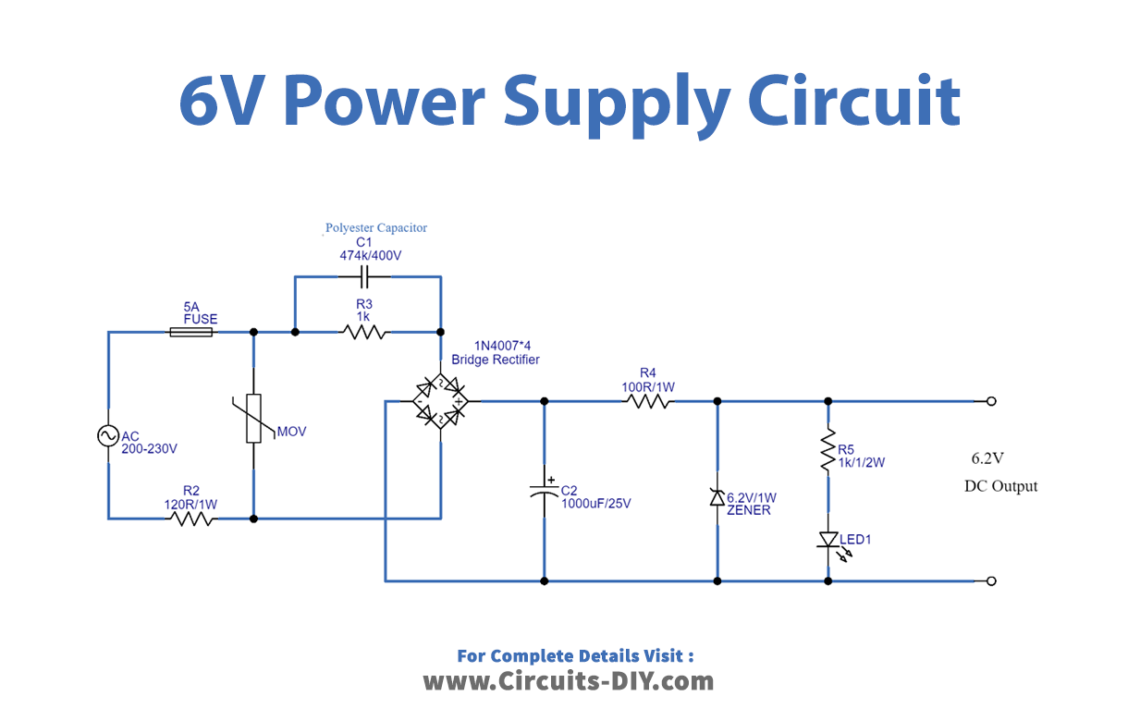
Working Explanation
This transformerless power supply is designed to produce a 6V DC output. It accepts an AC input between 200 and 300 V. The X-Rated capacitor C1 is connected serially with the AC mains phase line through a fuse.
The R2 is wired in parallel to the C1 to discharge the energy when there is no AC supply. The MOV, a metal oxide varistor, is connected to protect the circuit from sudden power and voltage spikes.
The existence of a DC supply is shown by a LED connected across the bridge rectifier’s output DC. The rectifier was constructed with four 1N4007 diodes, and its output is connected to filter capacitor C2.
The DC voltage is then controlled using a Zener diode. Changing out the Zener diodes with those of varying ratings allows us to vary DC voltages.
Application and Uses
- LED bulbs
- Toys
- Household appliances
- Emergency lights
- Television receivers
- ADC converters
- Digital communication systems, etc.