Introduction
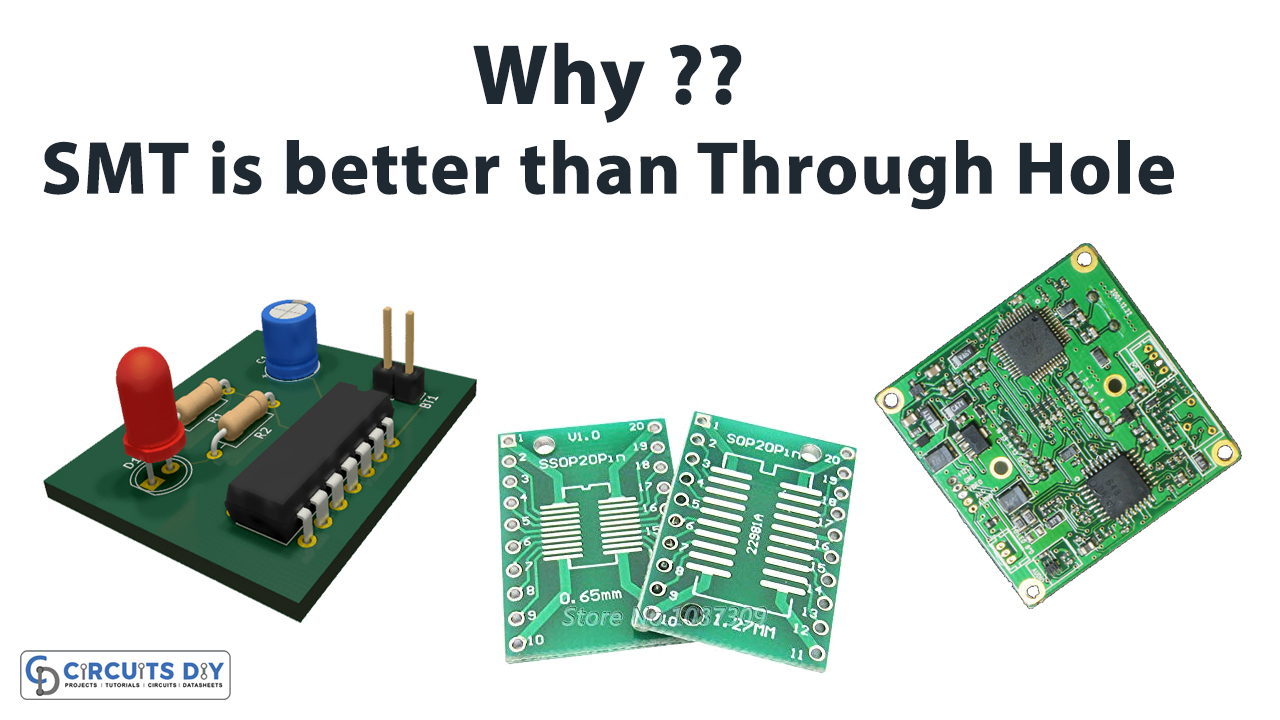
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) have played an important role in everyday life, from consumer electronics to high-performance systems. Surface Mounted Technology (SMT) and Through-Hole Technology (THT) are two important mounting techniques in PCB manufacturing over the years. SMT became increasingly prevalent and superior soldering procedure in technical products in the early 1980s. The traditional Through-hole technology has become outdated as electronics have become smaller and more capable, making them more compact. To learn more about the differences between the two technologies, and Why SMT is Better Than Through Hole Technology, we are here with this article.
What is Through Hole Technology?
Through-Hole Technology Mounting (THT) is the method of employing plated through holes to mount components with leads on a PCB. All components were mounted to the PCB with leads running through component holes in the board before the invention of SMT (Surface-mount technology). Until the end of the 1980s, this technology dominated the industry. THT components are extremely easy to alter while prototyping, making them ideal for testing and hobbyists.

Drawbacks with THT Technology
The necessity to drill many holes in the board is one of THT’s biggest drawbacks. This lengthens the production process and raises the cost of production. While the holes are important to keep components in place, they also limit the amount of space and routing area available for signal tracing.
Growth of SMT Technology
The amount of automation for PCB assembly for boards used in a range of devices began to grow in the 1970s and 1980s. The usage of conventional components with leads made PCB construction difficult. The leads of resistors and capacitors had to be pre-formed to fit through holes, and the leads of integrated circuits had to be fixed to the correct pitch to go through the holes.
What is SMT Technology?
Surface Mounted Technology allows electrical components to be mounted directly on the Printed Circuit Board’s surface (PCB). On smaller devices, designers use this kind of manufacturing. As a result, we consider it as the superior approach. This mounting method necessitates little or no hole drilling in the circuit board assembly. As a result, high connection density is achievable, as holes do not clog the routing region on the inner or rear side. In addition, the circuit board’s actual components are smaller and more compact. Surface mount technology became less costly than through-hole mounting as a result of this.

Advantages of SMT
- This method creates a strong bond between the components and the board.
- The board is capable of carrying and holding bigger and heavier components.
- It has the ability to withstand environmental stress.
- These types of boards are susceptible to greater temperatures.
- They have a long lifespan.
Difference Between THT and SMT

| Through-Hole Technology | Surface Mount Technology |
| The soldering is performed manually or automatically. | Soldering is automated |
| No pads or vias | It comprises vias and pads |
| This contains only the Through-hole test point | It can have both kinds of test points including THT or SMT |
| Needs larger footprints | Requires fewer footprints |
| Two-sided assembly is not common | Commonly used two-sided assembling |
| No stencils required | It needs stencils |
Why SMT is Better?
We’ve concluded that SMT assembly is more reliable and faster. On the other hand, it necessitates a thorough understanding of the whole procedure. It also includes requirements for the design phase. It can put together more components in a smaller space. As a result, it saves money and reduces errors. As a result, we’ve concluded that PCBs are continuing on the rise. Furthermore, in an era when designers are attempting to create tiny products, surface mount technology is a better fit.