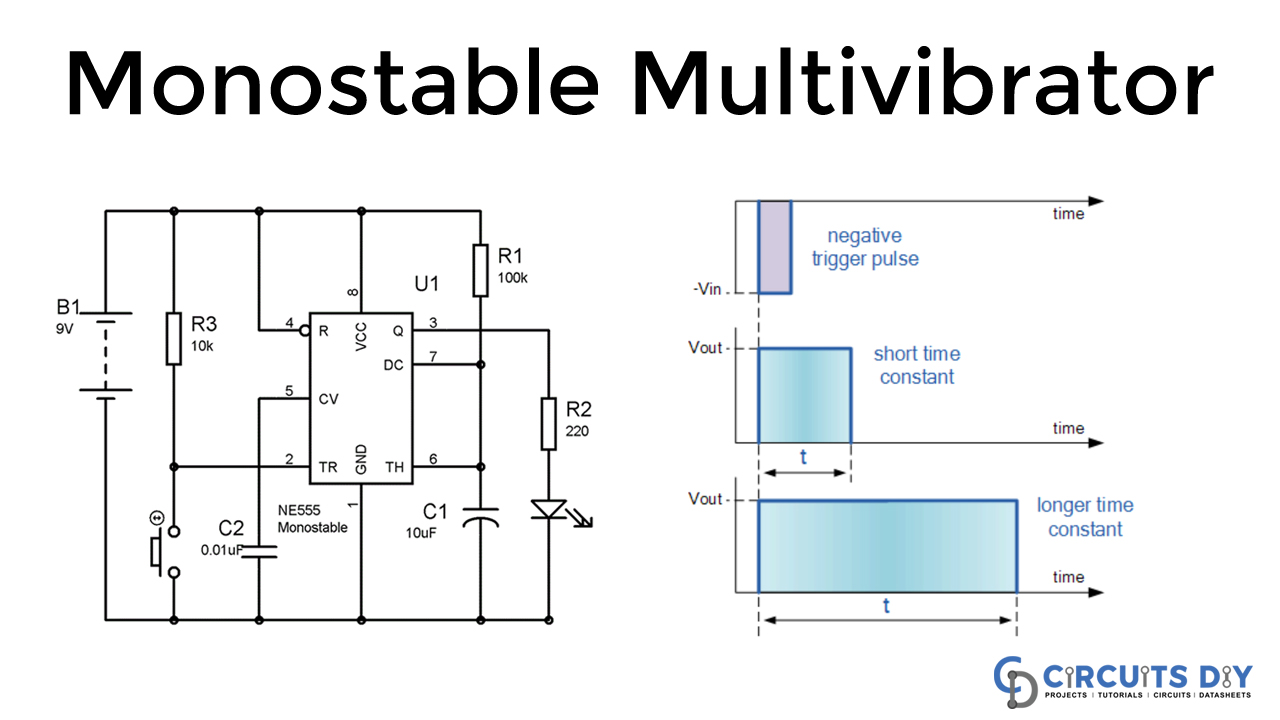
The monostable multivibrator mode of 555 timers IC is likewise called Single-shot mode. The single-shot mode is the other name of the monostable multivibrator mode of 555 timers IC. In this mode, just one state is steady, and the other one is unsteady, which is called an unstable or quasi-stable state.
The state of the 555 timer IC will be stable until the external triggering is applied. For progression from a stable to unstable state, external triggering is required. The ground pin is connected to the trigger pin utilizing a Push-button for providing the triggering.
So, in this tutorial, we are demonstrating the project of a 555 Timer Monostable Multivibrator Circuit, which is easy to make and requires a few components.

Hardware Component
The following components are required to make Monostable Multivibrator Circuit
| S. no | Component | Value | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | LED Diode | – | 1 |
| 2. | Switch | – | 2 |
| 3. | Battery | 9 V | 1 |
| 4. | IC | NE555 timer | 1 |
| 5. | Capacitor | 10uF, 0.01uF | 1 |
| 6. | Resistor | 10K, 100K, 220 Ohms | 1, 1, 1 |
NE555 IC Pinout

For a detailed description of pinout, dimension features, and specifications download the datasheet of 555 Timer
Monostable Multivibrator Circuit

Circuit Operation
In this section, we will discuss the circuit operation of the project 555 Timer Monostable Multivibrator Circuit in which we are displaying a monostable multivibrator mode of a 555 timer IC. In this project, we are using a few low-cost components such as capacitors, resistors, 555 timer IC, battery, switch, and LED diode. We have connected the LED to the output of the 555 timer IC for demonstrating the monostable mode of the 555 timer IC. When we press the push button, the LED will glow and automatically off after a certain time T, which we have calculated using this formula.
T= 1.1 x 100 K x 10 uF = 1.1 sec
Applications and Uses
The 555 timer IC is an 8-pin IC that can be worked as a monostable to create an assortment of uses i.e
- LED and lamp flashers
- Pulse generation
- Alarms
- Tone generation
- Logic clocks etc