Introduction
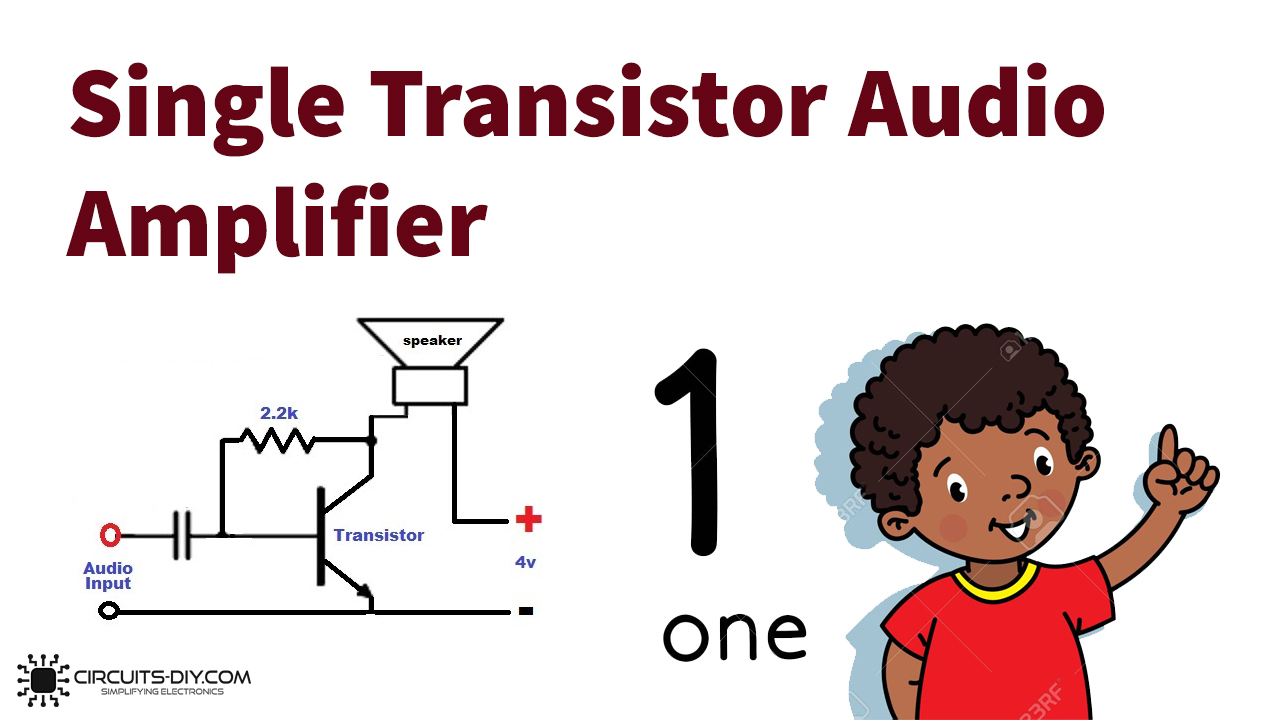
The single transistor amplifier circuits usually understand basic amplifiers and their different configurations. The circuit is easier to make but trickier to understand. Because, a single transistor amplifier can be made with three different configurations, common base, common collector, and the most widely used common emitter. Since the common emitter is extensively popular, therefore in this, article we will build a common emitter configuration.
In this arrangement, the input is provided at the base, the output is taken at the collector while the emitter remains ground or you can it’s common. Know that the amplifier circuit also has different classes, like class A, B, AB, C, D, etc. In this tutorial, we are making the class A single transistor amplifier.

Hardware Components
The following components are required to make Audio Amplifier Circuit
| S.no | Component | Value | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Electrolytic Capacitor | 22uF | 1 |
| 2. | Resistor | 2.2k | 1 |
| 3. | Transistor | 2N3904 | 1 |
| 4. | Battery | 4V | 1 |
| 5. | Speaker | 4 ohm | 1 |
2N3904 Pinout
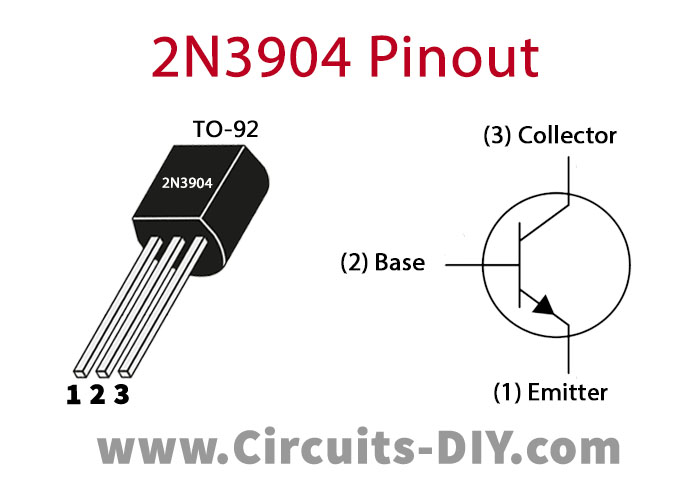
For a detailed description of pinout, dimension features, and specifications download the datasheet of 2N3904
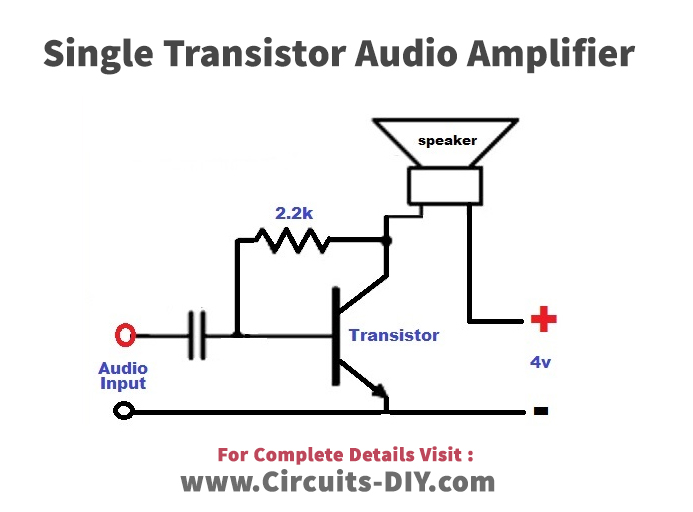
Audio Amplifier Circuit
Working Explanation
This single transistor amplifier circuit is very simple to make. It employs the Simple BC547 Transistor. 2.2K Resistor is the base resistor for this transistor., provides an audio signal at the base of the transistor which allows to flow of the current between collector and emitter. Capacitorwired in this circuit isolates the base of the transistor from the input source. Now that the base current or the voltage cannot affect the input audio. When input audio is provided at the base of the transistor, it goes into the forward stage. During the whole audio cycle that is provided to the transistor, it generates the maximum amplitude at the output side.
Application and Uses
- It can be utilized in children’s toys.
- can be adopted for different audio electronic devices.
- For portable devices.
- In the circuits that don’t require much higher gain.