Transformers are widely used for converting AC voltage for step-up or step-down voltage purposes. But for converting the DC voltage values from one value to another, we cannot use transformers. Therefore, in such applications where one needs to increase DC voltage, usually, a circuit known as a voltage multiplier or voltage booster is used. In voltage multiplier circuits, 555 timer IC is used which is configured as an astable multivibrator to supply the input for the circuit created using the diode and capacitor network. These voltage multiplier circuits are widely used in many electrical and electronic circuit applications such as in microwave ovens, strong electric field coils for cathode-ray tubes, electrostatic and high voltage test equipment, Etc., where it is required to have a very high DC voltage generated from a comparatively low rectified DC input supply.
Hardware Required
| S. No | Component Name | Value | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Timer IC | NE555 | 1 |
| 2 | Resistor | 15K, 27K | 1, 1, 1 |
| 3 | Diode | 1N4001 | 2 |
| 4 | Capacitor | 0.01uF, 330uF, 470uF | 2, 2, 1 |
| 5 | Battery | 12V | 1 |
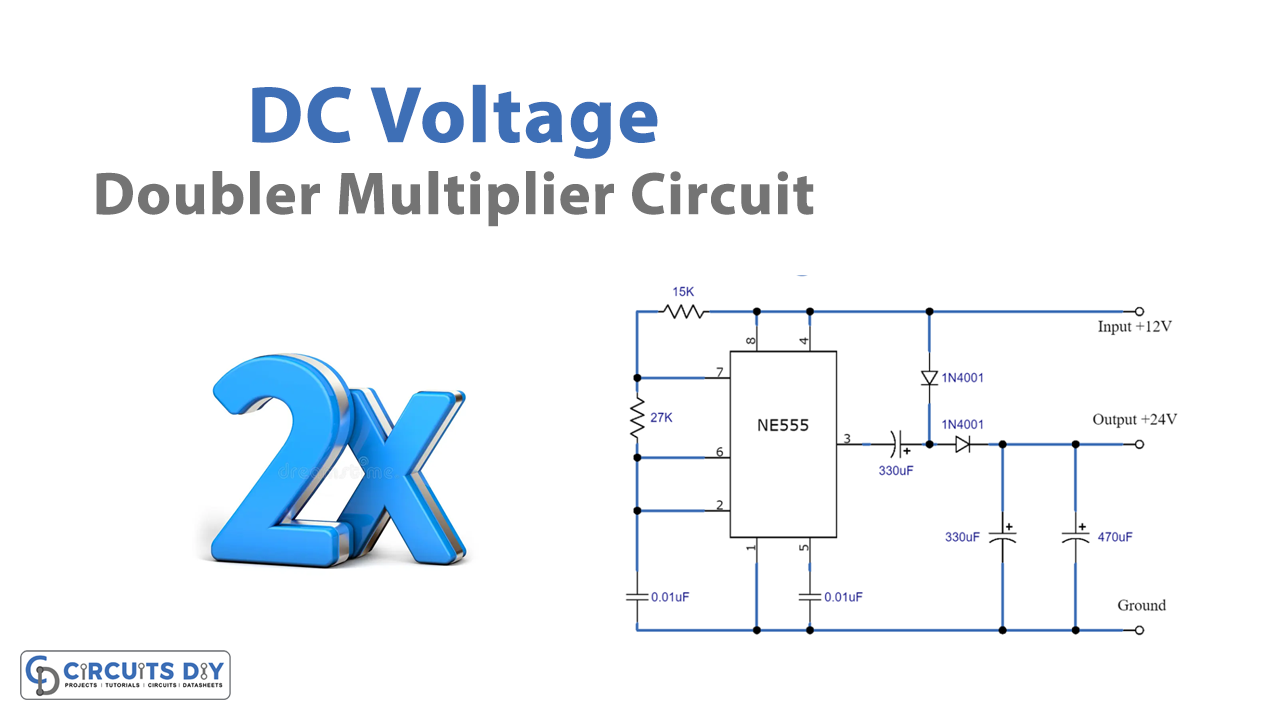
Circuit Diagram

Working
In this circuit, the 555 IC is working to produce short pulses of DC electricity which passes through capacitors, and diodes and thus multiplies the voltage. This voltage doubler circuit multiplies the supply voltage and produces an output that is approximately twice the voltage value of the input voltage.
When the output at pin 3 of 555 IC is low, the 330µF capacitor charges up to the supply voltage through diode, D1 while diode D2 will be off. When the output of pin 3 of 555 goes high, the voltage across 330µF discharges through diode D2, while D1 is reverse biased, adding its voltage to the source voltage and capacitor. The timing cycle from the 555 changes states again from HIGH to LOW and the cycle repeat once again, thus producing a DC load voltage that is twice the original input voltage.
Applications and uses:
Voltage multiplier circuits are widely used in many electrical and electronic circuit applications such as in microwave ovens, TV sets, lasers, air purifiers, industrial smoke-stack dust removers, strong electric field coils for cathode-ray tubes, electrostatic and high voltage test equipment, etc, where it is required to have a very high DC voltage generated from a comparatively low rectified DC input supply.