Introduction
In a world where electronics reign supreme, batteries are the lifeblood that keeps them functioning. Lead-acid batteries hold a special place among the many types of batteries available. They remain a steadfast choice for many applications. However, charging these batteries quickly and efficiently is a challenge that needs to be tackled.
In this post, we’ll take a deep dive into a high-power lead-acid battery charger circuit that can charge your batteries at lightning speeds, all while providing foolproof protection against mishaps. So, buckle up, and let’s charge into the world of lead-acid battery charging!
Hardware Required
| S.no | Components | Value | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IC | L200 | 1 |
| 2 | Transformer | 12V 600mA | 1 |
| 3 | Resistor | 1, 820, 560, 470 | 1, 1, 1, 1 |
| 4 | V. Resistor | 500 | 1 |
| 5 | Polar Capacitor | 1000u, 1u | 1, 1 |
| 6 | Non Polar Capacitor | 330 | 1 |
| 7 | Battery | 12V, 6V | 1, 1 |
| 8 | Diode | 1N4001, 1N4148 | 2, 2 |
| 9 | Diode Bridge | 1N4001 | 4 |
| 10 | Fuse | 100mA | 1 |
| 11 | Switch | – | 2 |
| 12 | Coil meter | 500mA | 1 |
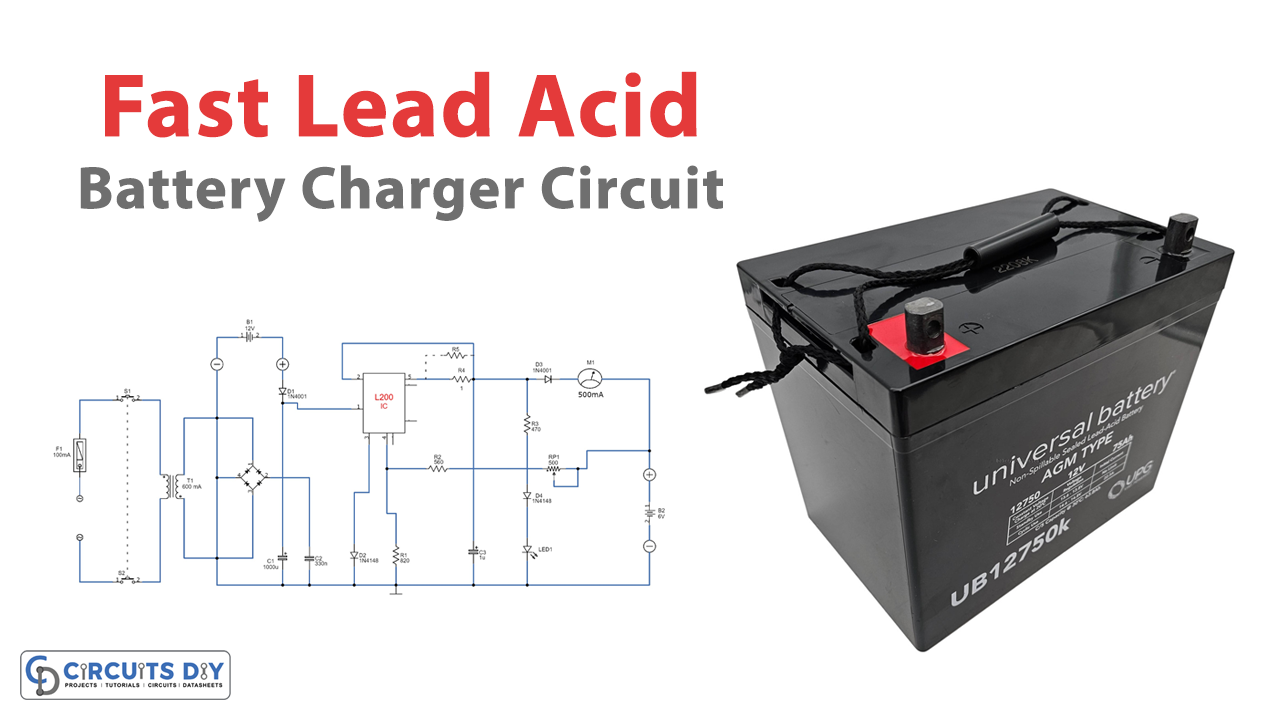
Circuit Diagram
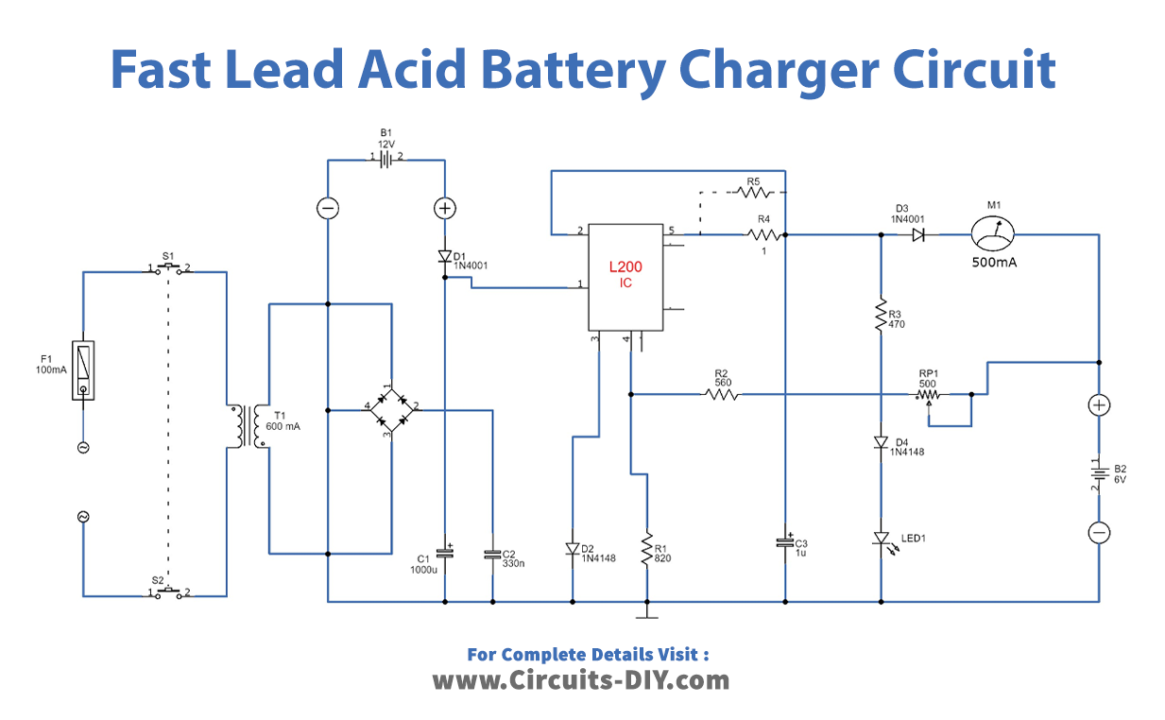
Circuit Operation
The lead-acid charger circuit uses an IC L200 voltage regulator to maintain a consistent charging voltage. When there is no battery, P1 sets the voltage. R1 and R2 resistors limit the current, and R2 is needed only for a charging current over 0.5 A or to allow for a more precise output current. The current stays within 0.45 (R1+R2)/R1R2 A, displayed by M1. The mains or a 12V car battery can power the circuit. The L200 does not require a heat sink, but one can be added if desired.
The charging current does not need to be within the 0.1-1C range for fast-charging lead-acid batteries using this circuit. Instead, when the charging current drops to 1% of its capacity, the battery is assumed to be fully charged. A 6V battery requires a charging voltage of 6.9V, while a 12V battery requires 13.8V.
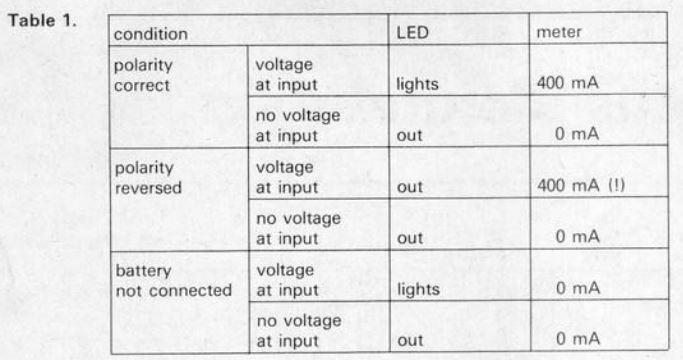
Some Potential Issues
Table 1 lists some potential issues that may arise while charging, but these do not apply when the battery is flat. In such cases, the battery’s correct connections to the charger terminals must be verified.
Variations for Different Battery Types
Table 2 displays the circuit variations for different types of 6V batteries. The safest way to charge a battery is to keep the charging current at or below 1/10 of the battery’s capacity in Ah.

Conclusion
As we wrap up this post, we hope you’ve gained a newfound appreciation for lead-acid batteries and their usefulness in electronics. While they may not be as flashy as their NiCd counterparts, they indeed hold their own regarding providing reliable power. And with the high-power lead-acid battery charger circuit we’ve explored, you can now charge your batteries quickly and safely without any worries about mishaps.
So go forth and power your projects confidently, knowing your batteries are in good hands. We hope you’ve enjoyed this tutorial and found it helpful. Until next time, keep exploring the exciting world of electronics!