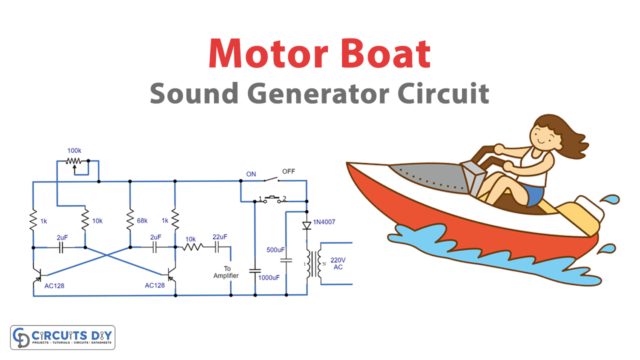
Introduction:
The transformer is known to be a device that transfers energy from one alternating-current circuit to another by means of electromagnetic induction. It either steps up the voltage or steps down the voltage depending upon the number of coils at the primary and secondary sides. A transformer has no movable parts and is thus called a static device. It is a very useful device and has a large range of applications. The basic classification of transformer is a step-down transformer and step-up transformer.
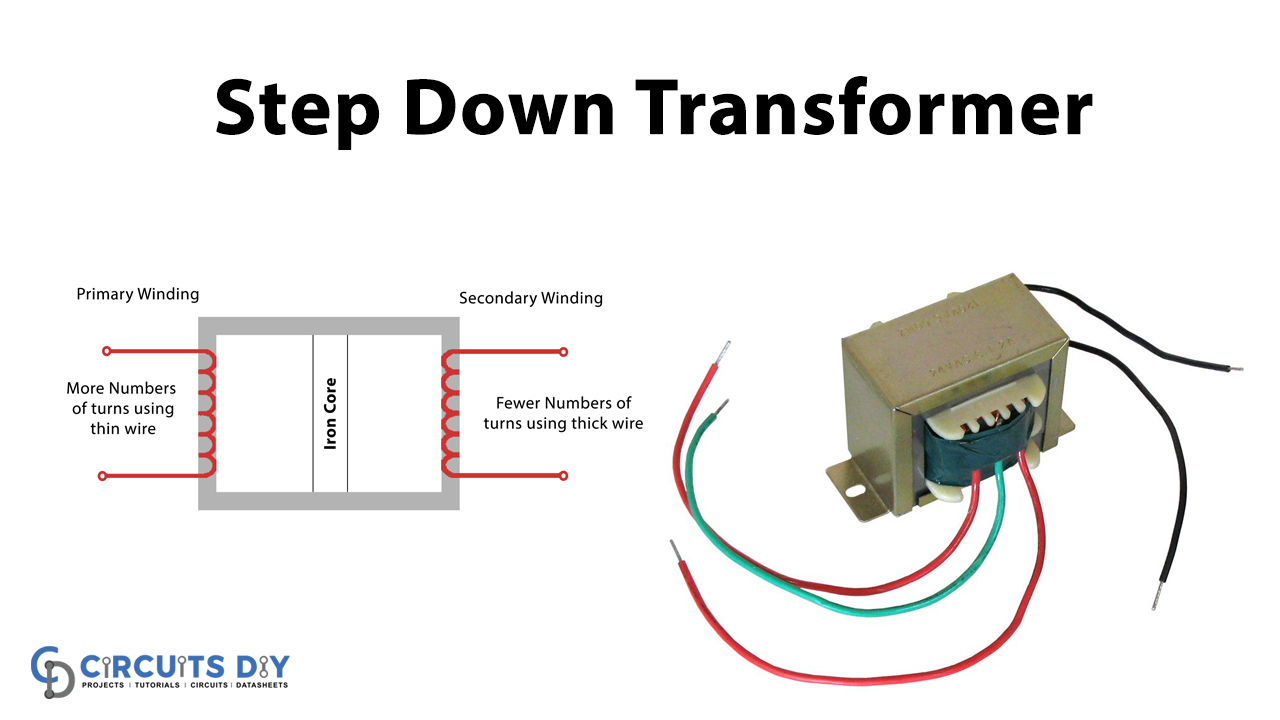
A step-down transformer is a type of transformer that decreases the voltage at the secondary side which is received at the primary side. The step-down transformers are applicable for a wide variety of real-world applications. For a step-down transformer, the secondary windings are fewer than the primary in order to reduce the voltage taken as an input by the primary coils.
Parts:
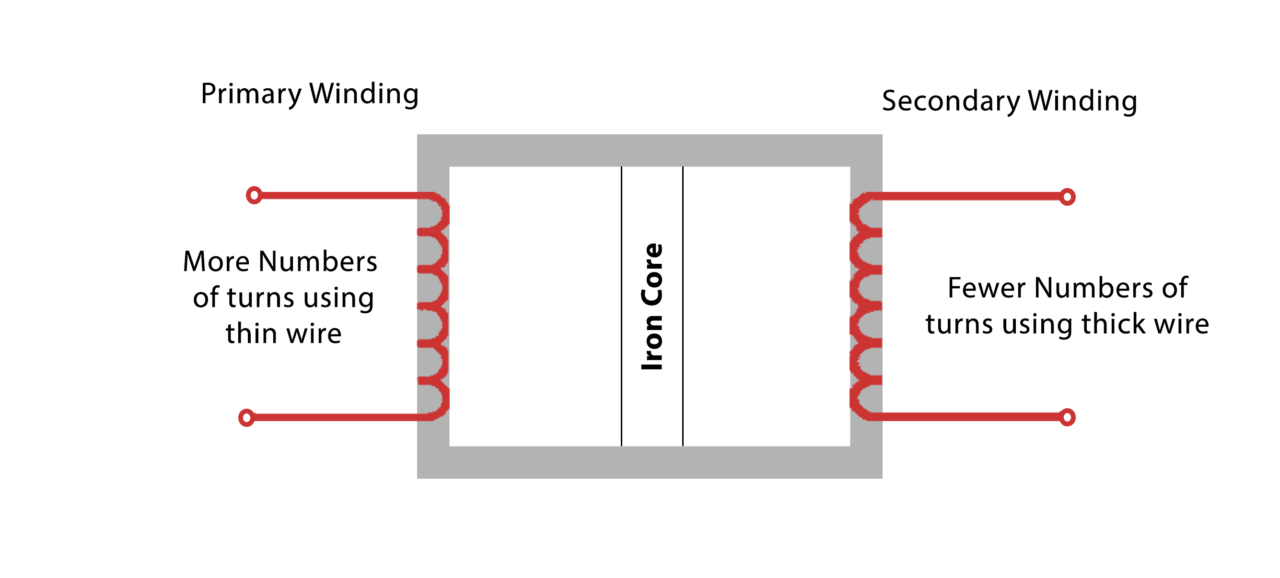
The figure below shows the parts of the step-down transformer. It includes primary windings, secondary windings, and an iron core. The core is made of separate plates in order to avoid eddy current losses. The secondary windings are fewer than the primary and are made of thicker wire.
Symbol:
The three symbols of the transformer are shown in the figure below:
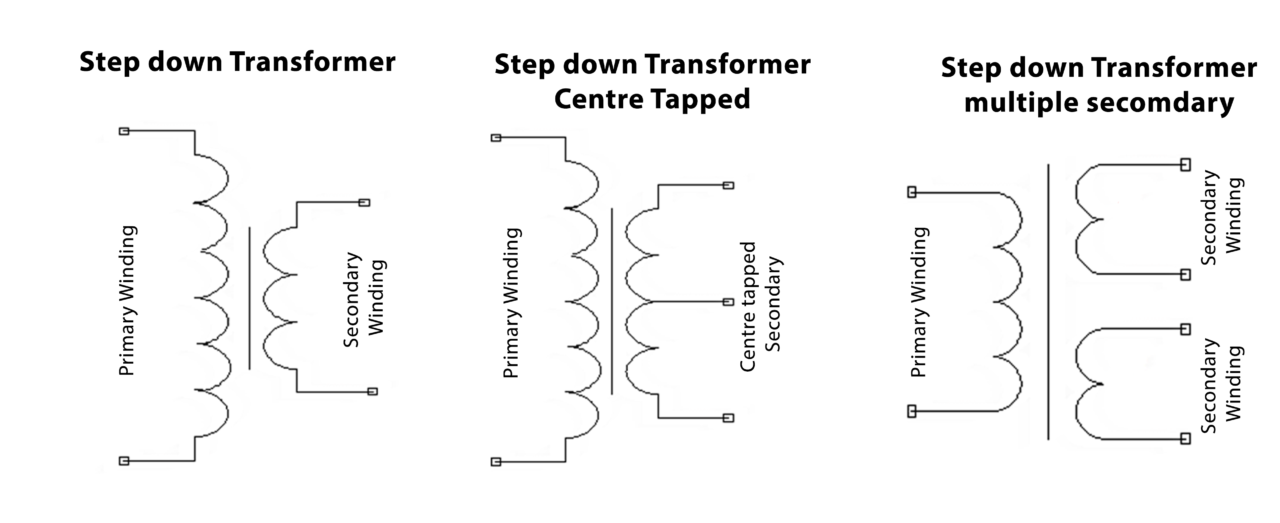
The step-down transformer has the primary and secondary windings which are made up of insulated copper wire while the magnetic core is made up of iron or ferrite. It outputs the step-down and low amplitude power through two wires.
The second figure is the denotation of a step-down center-tapped transformer in which the secondary winding is split into two halves. It delivers two secondary outputs as follows 12V-0-12V.
The third figure denotes step-down transformer multiple secondary. It has a primary winding and can have two or more secondary windings and outputs two or more voltage depending on the number of secondary windings as 0-12V, 0-18V, etc.
Working Principle:
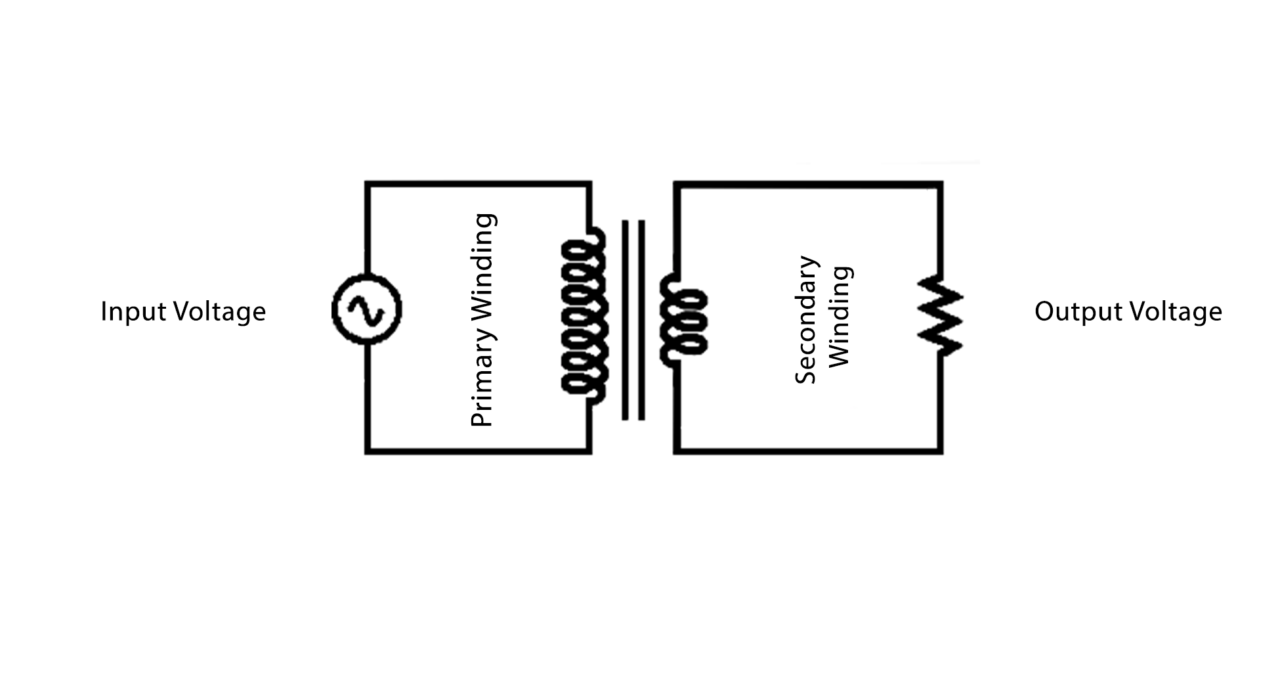
The input is applied to the primary coil of the transformer while the secondary coil is coupled with the load. Hence, the step-down output voltage from the secondary coil is transmitted to the load.
When the input is applied to the transformer, it will excite the primary windings and the voltage circulate across the windings which develops the magnetic flux all over the magnetic core. As the secondary coil is connected to the magnetic flux, it will induce electromagnetic force in the secondary coil based on Faraday’s law of mathematical induction. The number of windings at the secondary defines the strength of the voltage during the supply of the magnetic flux.
Hence, without any electrical contact between the two windings, the voltages are supplied to the secondary coil.
Applications:
There is a wide variety of applications of step-down transformers. It includes:
- Power distribution networks
- Home appliances
- Voltage stabilizers
- Rectifier and inverter circuits
- Power supplies
- Medical equipment
- Chargers and adapters
- Transmission lines and many more.
Advantages:
The step-down transformers are highly reliable and durable, cost-effective, highly efficient, and provide different supply voltages.